What is Native Resolution in Video
Each display or monitor is not just 5, 11, 17 or more inches, but also the physical number of columns and rows of pixels that make up a screen’s image.

The native resolution meaning
Let’s start with the native resolution definition. To make it short, it is the number of pixels in each dimension. For example, the resolution of 1920 x 1080 means that there are 1920 pixels horizontally and 1080 pixels vertically.
As for the aspect ratio, it is the proportional relationship of width to height. It helps to understand the overall shape of the picture and usually looks like this — 1:1 (this video is square), 16:9 (this one is horizontal), 9:16 (this one is vertical).
In theory, the more pixels, the sharper is the visual. However, to see the so-called pixel perfect picture, it is important that the input resolution and aspect ratio of the video you are watching match the display characteristics.
If the resolution doesn't match up, then you might see a lower quality or distorted picture. If the aspect ratio is not right, you may see black bars on the top and bottom (also called letterboxing) and sides of the screen (also called pillarboxing).
Let's have a look at most common resolutions and aspect ratios we can meet in the following cases:
Native resolution and aspect ratio in films
When it all started, movies were in a 4:3 ratio which was determined by the 35mm analogue film stock used for moving pictures. Their resolution can only be approximately estimated at about 5600 x 3620 pixels because much depended on the type of film grain and its processing method.
These days the most common aspect ratio for films is 16:9.
There have been other aspect ratios in between — 1.37:1 (Academy Ratio), 2.59:1 (Cinerama), 2.35:1 (CinemaScope), 2.2:1 (Super Panavision 70), 1.43:1 (IMAX), and more. When used these days by some filmmakers, these aspect ratios are more a stylistic choice.
Native resolution and aspect ratio on TV screens
The 4:3 aspect ratio was also a traditional TV standard years ago, while 16:9 is a standard for these days.
As for the resolution, it could be different depending on the TV set specs:
- SD (standard definition): 720 x 576 pixels
- 720p HD: 1280 x 720 pixels
- 1080p Full HD: 1920 x 1080 pixels
- Quad HD: 2560 x 1440 pixels
- Ultra HD: 3840 x 2160 pixels
- 4K: 4096 x 2160 pixels
- 5K: 5120 x 2880 pixels
- and even 8K: 7680 x 4320 pixels
Native resolution and aspect ratio on smartphones
The 16:9 aspect ratio is one of most common on smartphones as well. However many apps can use different ratios for the videos — for example, Instagram posts can be 1:1, 16:9, 9:16, 4:5.
As for the native resolution, there is really a wide range of them. It can start from 768 x 1024 and the number of pixels can be growing with every next model.
When thinking about smartphone specs, it is always a good idea to check the specific media requirements to make sure your movie fits perfectly both in terms of aspect ratio and resolution.
How to change video aspect ratio
If you are not sure about your device’s specs, you can always find this information in the manual or consult the manufacturer’s website on how to check native resolution or aspect ratio.
If you need to make changes in your film, continue reading to learn how to change native screen resolution or aspect ratio the easiest way.
With one of many Clideo’s video editing tools you can adjust these settings online, in any browser and on any platform, including Windows, Mac, Linux, Android, and iOS.
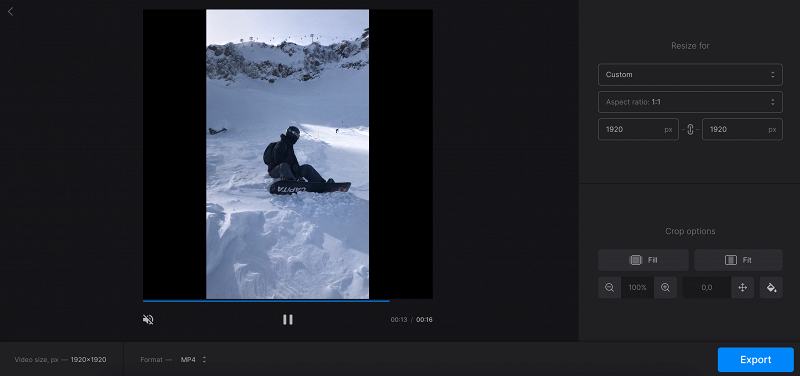
- Open the video resizer tool in your browser and upload the file from your device or cloud storage.
- Then, select the social medium and a post type you need. Alternatively, choose “Custom” to select the aspect ratio and set the resolution manually. Change the “Crop options” settings, if needed, and then hit “Export”.
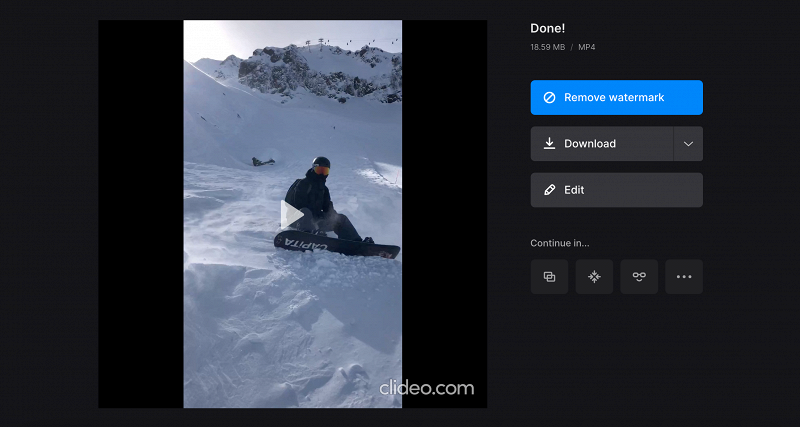
- Finally, review the result and download the file back to your device, or save it to Google Drive or Dropbox. You can also click the “Edit” button to try other settings.

We are regularly improving our tools to add new features or enhance your experience. Check our Help Center for the most recent instructions.



